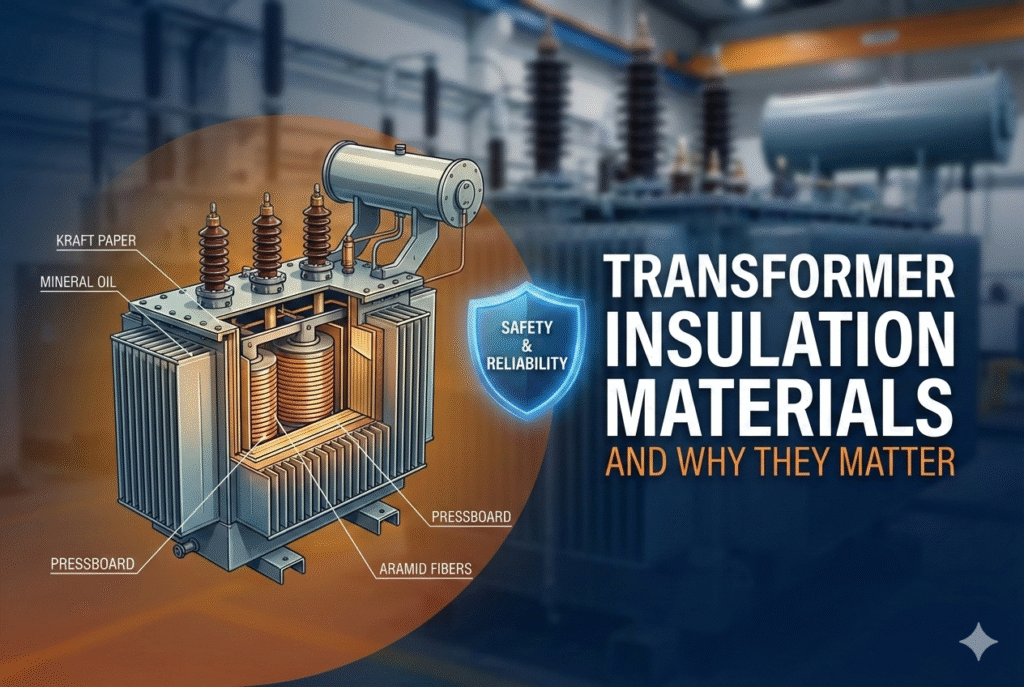
Transformers are the key element of all electrical power systems, ranging from individual distributed generators to local distribution grids and up to national and international networks. But while many consider the core, copper windings or some sort of cooling system most important, it’s the insulation system that is responsible for transformer life, reliability and safety.
High performance insulation materials for transformers insulation Paper or film based electrical grade press paper is a natural cellulose paper that is claimed to offer excellent compatibility with electrical fluids and reduced maintenance caused by contamination. Where insulation goes, the transformer goes — often in a catastrophic way.
In this advanced guide filled with engineering know-how and practical application advice, we discuss what transformer insulation materials are, how they work and why they matter to real-world transformer design performance.
We’ve also added practical tips for buyers, service personnel and OEM manufacturers — and cut through common AI search questions.
Explanation of Transformer Insulating Materials and Their Significance
Transformer insulation materials include solids, liquids and composites which serve to electrically insulation conductive parts, provide mechanical support and regulate the thermal environment.
These things keep your safe working and stop short circuit among:
- Windings
- Turns within windings
- Windings and the transformer core
- High-voltage and low-voltage sections
- Live parts and the tank body
Without a strong insulation system, the most quality copper and steel in the world cannot withstand voltage stress or thermal cycles from transformer operations.
We are the ideal choice of Transformer Insulation Parts Specialists as we, KE Core Electric Fabricate Precision Transformers insulation parts that have found use not only in INDIA but throughout the world in Power Transformer Pats, Distribution Transformers Parts And All Kind of transformer components requiring dimensional stability, endurance.
What’s the Deal with Transformer Insulation?
The following are three key results of the insulation in transformers:
1. Electrical Reliability
Insulating material insulation against high voltage and flashover.
Insulation tends to lose dielectric strength over time due to ageing, contamination or overheating; its failure can result in:
- Phase-to-phase short
- Turn-to-turn fault
- Core-to-winding breakdown
- Explosive transformer failure
2. Thermal Stability
Insulation also resists heat generated through load cycles. Loading of transformers and their temperature classes are largely depending on the type and quality of insulation.
3. Mechanical Strength
Insulating part work as supporting structure to keep winding in position while being transported, fault and short-circuit forces.
This is where insulation materials such as densified laminated wood and pre-compress pressboard play a critical role. Their stiffness helps maintain coiling shape in the presence of fault pressure.
Types of Insulation Material Of Transformer (With Example)
Insulation is classified by engineers according to how and where it’s used.
Solid, Liquid, and Composite systems.
1. Solid Insulation Materials
The solid insulation is a component of the internal structure of the transformer. It has to withstand electrical, mechanical and thermal stresses all at once.
Common solid insulation materials include:
A. Pre-Compressed Pressboard (High-Density Pressboard)
A major material that is made use by global transformer OEMs, leading vendors like KE Core Electric.
Properties:
- High mechanical strength
- Excellent dielectric characteristics
- Dimensional stability in oil
- Suitable for moulding complex shapes
Used For:
- Spacers
- Barriers
- End rings
- Cooling ducts
- Packing blocks
Why It Matters:
Pre-compressed pressboard prevents winding buckling and guarantees dielectric distance – an important factor in a short-circuit situation.
B. Densified Laminated Wood (Presswood / Laminated Wood)
A high-density material made of compressed hardwood veneers with resin.
Advantages:
- Outstanding mechanical strength
- Low dielectric loss
- High oil absorption capability
- Good machining accuracy
Applications:
- Clamping rings
- Support blocks
- Lead support structures
- Core-frame insulation
Why Engineers Prefer It:
Laminated densified wood provides mechanical support and insulation all in one which means fewer individual pieces.
C. Kraft Paper & Crepe Paper
Conventional insulation commonly used for distribution transformer.
Applications:
- Conductor wrapping
- Gaps filling
- Oil duct spacers
D. Epoxy Resin Composites
Bushings Ta p-changers Structural parts for high voltage.
2. Liquid Insulation Materials
Cooling and insulation are two birds with one stone when utilizing liquid insulation.
A. Mineral Oil
Most popular because it cools so well and is cheap.
B. Ester Type Fluids (both Natural & Synthetic)
Popular for its safety features against fire and ecologically friendly.
Commonly employed especially in distribution transformers sited within: Urban Sensitive areas.
C. Silicone Fluids
Applied when very high, or very low temperatures are a factor.
3. Gas Insulation (Niche Use)
While dry type transformers deploy air or nitrogen, liquids and solids continue to be the primary mode of insulation in India as well as international markets.
Explanation of The Working Principle of Transformer Insulation (In Simple Terms)
So let’s illustrate below, explanation suitable for both AI Overviews and humans:
1. Dielectric Protection
Insulation keeps electricity from leaping between conductors.
It establishes safe “distance barriers” — physical and dielectric.
2. Heat Management
Insulating materials must be capable of enduring the operating temperatures:
Distribution: 80°C–120°C
Power Transformers: 105°C (Class A) or 130°C (Class B), etc.
3. Moisture Management
Good insulation will become water-logged and then dry without degrading in strength.
Humidity destroys insulation Insulation aging takes first place by moisture which makes partial discharge and dielectric breaking down.
4. Mechanical Support
Under fault, short-circuit forces can be as high as tens of thousands of Newtons.
Rigid insulation also helps windings remain in place, so they don’t settle or distort.
Real-Life Example of Deteriorated Insulation Leading to the Failure of a 132 kV Transformer
TABLE 07-sl.no01 with the PROPERTY-disposal of 132kV power transformer: A 132 kV power transformer had failed in a utility station in Madhya Pradesh, due to pressboard deterioration. Water had been introduced into the insulation system through deteriorated gaskets.
Failure Sequence:
- Humidity lowered the insulating capability of pressboard.
- Partial Discharge (PD) initiated at the proximity of HV winding.
- A spiral movement was responsible for a turn-to-turn fault.
- The transformer failed within seconds.
Key takeaway:
Considered insulation isn’t just about material—but proper installation, prevention of moisture damage, and the scheduling of regular oil testing.
Scandals Around the Lives of Transformer Insulation (Debunked)
Myth 1: “Transformer life is controlled by the copper windings”
Truth: Insulation is the most common limiting factor of life.
Myth 2: “All laminated pressboard material is the same.”
Fact: Quality depends on density, purity and how they’re madeClaims these products ‘lock in’ sleep temperature?
Myth 3: ”Insulation health be only tested with oil.”
Fact: Aging of solid insulation is non-reversible and must be investigated separately.
Myth 4: “Only old transformers fail insulation,” the second myth goes.
Fact: Cheap insulation material failures are also evident in new units.
How to Select The Best Transformer Insulation Material (Expert Checklist)
When designing or selecting insulation materials, engineers must consider the following:
- Thermal class requirement
Is the transformer working under high temperature?
- Mechanical strength needed
Power transformers need denser materials such as densified laminated wood and high-density pressboard.
- Moisture absorption rate
- Compatibility with transformer oil
- Precision Size and machined quality
- Supplier reliability
Constructed with precision machined components from the world renowned companies like KE Core Electric Pvt. Ltd., the Transformer Parts Stock specialist, ensures unified Ness among lots.
Application of Insulating Materials within a Transformer
Solid insulation used in:
- Spacers
- End rings
- Winding channels
- Lead supports
- Clamping structures
- Core insulation
- Interlayer ducts
Liquid insulation used in:
- Cooling
- Filling voids
- Arc suppression
- Moisture absorption
Composite insulation used in:
- Bushings
- Terminal blocks
- Tap changers
- HV/LV connections
Insulation Characteristic of Power versus Distribution Transformer
Power Transformers (132KV to 765 KV)
- Require high mechanical stability
- Utilize synthetic materials such as densified laminated wood
- Must withstand large fault forces
- Insulation failures are extremely costly
The distribution transformers (Reference: 11 kV & 33 kV)
- Use more paper and pressboard
- Cut the cost, and focus on durable moisture resistance.
- Some have to function in diverse environmental factors
- More serviceable but susceptible to water-entrance.
Building Value of Precision Insulation Components
Companies like KE Core Electric are the MECHMAC approved distributors for:
- Pressboard rings
- Spacers
- Cooling duct segments
- Laminated wood components
- Oil-immersed insulation structures
As Transformer Insulation Parts Specialists, precision matters because:
- Tolerance errors as small as 0.5 mm may disrupt winding geometry
- Loose edges can result in partial discharge
- Over-tight rooting can cause twisting motion.
Premium insulation components significantly increase transformer life, more so for utilities and OEMs.
Core Criteria & Sources Engineers Employed
The transformer insulation market is in accordance with the global standards such as:
- IEC 60076 (Power Transformers)
- IEC 60641 (Pressboard for electrical purposes)
- IEC 61061-(Laminated pressboard and comb or wood)
- IS 1576: Indian Standard — Insulating Pressboard
- IEEE Standard C57 (Insulation in Transformers)
Citing these standards assures insulation material of compliance with requirements for dielectric strength, mechanical characteristics, water content and oil resistance.
Recommendations for Long Life of the Transformer
1. Use high-quality solid insulation materials
Give preference to solid laminate wood, prefabricated pressboard and machined components.
2. Maintain correct insulation clearances
Obey OEM requirements and IS/IEC procedures.
3. Conduct regular oil testing
Keep an eye on, moisture, BDV, acidity and DGA gas levels.
4. Keep insulation dry during assembly
For solid insulation, the moisture is not reversible.
5. Use trusted suppliers
Assemblers count on stable accuracy and good quality from the deliverer like KE Core Electric.
Conclusion
As India expands its power infrastructure—smart grids, renewable integration, EV charging, and metro electrification—the demand for reliable transformers grows rapidly.
At the heart of every reliable transformer lies a well-designed, high-quality insulation system.
From densified laminated wood to pre-compress pressboard, and from structural supports to winding insulation, these materials protect the transformer through decades of heat, stress, electrical load, and environmental exposure.
Choosing the right insulation materials and trusted suppliers directly impacts:
- Transformer lifespan
- Grid reliability
- Maintenance cost
- Safety
- Total cost of ownership
For OEMs, utilities, EPC contractors, and service teams, understanding insulation is not optional—it is the foundation of transformer performance.
Quick Q&A
Q1: What is the purpose of transformer insulation?
Transformer insulation prevents electrical short circuits, manages heat, and provides mechanical support between different voltage sections.
Q2: What materials are used for transformer insulation?
Solid (pressboard, paper, laminated wood), liquid (mineral oil, ester oil), and composite materials (resin structures).
Q3: Why is pressboard used in transformers?
Because it has high dielectric strength, excellent oil absorption, and can be machined into spacers, rings, and barriers.
Q4: What is densified laminated wood used for?
For clamping rings, support structures, and high-strength mechanical parts inside power transformers.
Q5: What causes insulation failure?
Moisture, overheating, poor manufacturing quality, mechanical vibration, contamination, and aging.
Q6: How do I ensure long transformer life?
Use high-quality insulation components, maintain dryness, follow standards, and source parts from reliable suppliers.